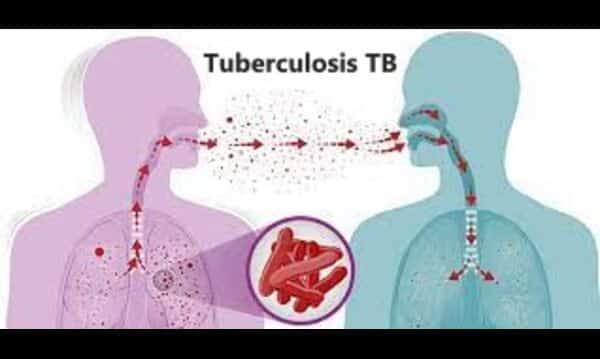
What Is Tuberculosis?
Humans can suffer from tuberculosis if they breathe in the microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). By the time TB affects the lungs, this disease is the most contagious and can spread to others by close contact.
Various Types Of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis infection (inactive tuberculosis)
An individual can have tuberculosis microorganisms in his body and never shows indications. In many people, the immune structure can contain microorganisms and do not cause infection. In this case, the individual will have TB but not a dynamic infection.
Does Inactive Tuberculosis Is Contagious?
Specialists refer to this as inactive tuberculosis. An individual may never experience side effects and be unaware of the infection. In addition, there is no danger of giving inert contamination to another person. In any case, an individual with inactive TB needs treatment.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) measure indicates that over 13 million individuals from reliable sources in the United States have inactive Tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Infection (Dynamic Tuberculosis)
The body may not be able to contain the microorganisms of tuberculosis. This is more normal when the resistance framework is weakened by disease or the use of prescribed prescriptions.
When this occurs, microorganisms can multiply and cause manifestations, resulting in dynamic tuberculosis. Individuals with dynamic tuberculosis can spread contamination.
Without clinical mediation, tuberculosis becomes dynamic in 5-10% TSR for infected individuals. In about half of these individuals, movement occurs within 2-5 years of infection, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Causes Of Tuberculosis
The microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes TB. It can be spread through the air in droplets when a person with respiratory TB sniffles, inhales, spits, chuckles, or talks.
- Tirelessly enlarged lymph axons, or “organ enlargement”
- stomach pain
- Joint or bone pain
- Chaos
- Industrious brain pain
- Seizures
- Poor living conditions
Symptoms Of Tuberculosis
A lethargic or lethargic individual will have no indications. You may have TB anyway, but the microbes in your body aren’t doing any harm yet.
- Loss of cravings and occasional weight loss
- Fever
- Goosebumps
- night sweats
- Intrusion into blood or body fluids (sputum) is an indicator of pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Bone pain may mean that microorganisms have attacked your bones.
These side effects can also occur with various infections, so see your medical care provider and let them know if you have tuberculosis.
Also, read latest information about COVID-19.
Risk Factors
The risk of dynamic tuberculosis formation is higher in the:
- Anyone with a worn-out resistance tire
- Anyone who initially cared for the disease after 2-5 years
- The more established old and young
- Individuals using injected sports medicine
- Individuals who have not previously received appropriate treatment for TB
How To Cure TB?
With early identification and synthesis of anti-infective agents, tuberculosis becomes treatable.
The appropriate type of anti-biotic and the length of treatment will depend on:
- Individual age and general wellbeing
- Regardless of whether they have inactive or dynamic TB
- Pollution area
- Regardless of whether the tuberculosis strain is safe for medicate
- Treatment for inactive TB can vary. This may include applying an antimicrobial once a week for some time or continuously for an extended period of time.
- Treatment of dynamic tuberculosis may involve taking a few medications for 6-9 months. When an individual has a safe drug strain of TB, treatment will be mind-boggling.
It is necessary to finish the full course of treatment, regardless of whether the side effects disappear. If an individual stops taking the drug early, some microorganisms can tolerate and become immune to anti-infective agents. In this case, the individual may initiate a safe TB drug booster.
Depending on the parts of the body that TB affects, the specialist may also recommend corticosteroids.
How To Diagnose Tuberculosis?
An individual with inactive TB will not have any manifestations; however, contamination can show up on tests. Individuals should request tuberculosis tests if:
- If they have close contact with an individual who is infected or at risk of contracting TB.
- Live in a country with high rates of tuberculosis.
- Working in a climate where TB may be available.
- The specialist will get some information about any indications and the individual’s clinical history.
- They will also do a physical evaluation, which includes paying attention to the lungs and checking for dilation in the lymph axons.
- To test for dynamic tuberculosis infection, a specialist may suggest a sputum test and a chest X-ray.
Risk Of Death From TB
Infection rates worldwide are calculated in the range of 7% to 35%. The retrospective review was directed from 2010 to the 2013 year.
Medication For Tuberculosis
These are the three treatment options:
In case you have this type of disease, you will need to take various anti-biotic agents for 6 to 9 months. These four medications are generally used to treat:
- ethambutol (myambutol)
- Isoniazid
- pyrazinamide
- rifampin
- Isoniazid (INH): This is the most well-known treatment for dormant tuberculosis. So, You usually take the anti-biotic pill isoniazid every day for a very long time.
- Rifampin (Refrain, Reactance): You have been taking this antitoxin medicine every day for a long time. It is a choice in case you have side effects or contraindications to INH.
- Isoniazid and rifapentine: You take each of these anti-infective agents once each week for a long time under the supervision of your PCP (personal care provider).
If only a few types of drugs don’t do this work, you have what specialists call “safe multidrug TB.” You will need to take a combination of medications for 20 to 30 months. They include:
- Anti-infective agents called fluoroquinolones
- Injectable antimicrobial, e.g., amikacin (Amici), streptomycin
More current antivenom drugs, for example, bed aquiline (Sertorius), ethionamide (Traitor), and corrosive para-aminosalicylic acid. These are given regardless of the different prescriptions. The new drug Pretomanid is used in connection with bed aquiline and linezolid, and scientists are still focusing on these prescriptions.